Muscles in the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
The anterolateral abdominal wall is composed of muscles that help to compress the abdominal viscera as well as contain increases in intra-abdominal pressure in instances of forced expiration, defecation, and childbirth.
External Oblique
These fibres run in a downwards and forwards direction. They originate on the 8 lower ribs and insert into the linea alba and iliac crest.
It acts to compress the abdomen.
Internal Oblique
These fires run in a backwards and downwards direction . They originate on two thirds of the iliac crest, inguinal ligament, and lumbodorsal fascia and insert into the linea alba, the 3 lower ribs, and the pubic and pectineal lines.
It acts to compress the abdomen and flex the trunk.
Transversus Abdominis
These fibres run transversely. They originate on the costal cartilage, the 7th to 12th ribs, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament and insert into the linea alba, pubic crest, and pectineal line.
It acts to compress the abdomen.
Rectus Abdominis
These fibres run in a superior to inferior direction. They originate on the pubic crest, pubic tubercle, and pubic symphysis and insert into the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs 5 to 7.
It acts to compress the abdomen and flex the trunk.
Pyramidalis
These fibres run in a superior to inferior direction. They originate on the pubic crest, pubic tubercle, and pubic symphysis and insert into the linea alba.
It acts to tense the linea alba.
Rectus Sheath
The rectus abdominis and pyramidalis muscles are both enclosed within the rectus sheath. It’s anterior wall is composed of aponeurosis from the external oblique muscle and half of the internal oblique muscle. It’s posterior wall is composed of the remaining half of the aponeurosis from the internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle.
Fascia
The superficial fascia below the region of the umbilicus separates into Camper’s facia (superficial) and Scarpa’s fascia (deep).
Muscles in the Posterior Abdominal Wall
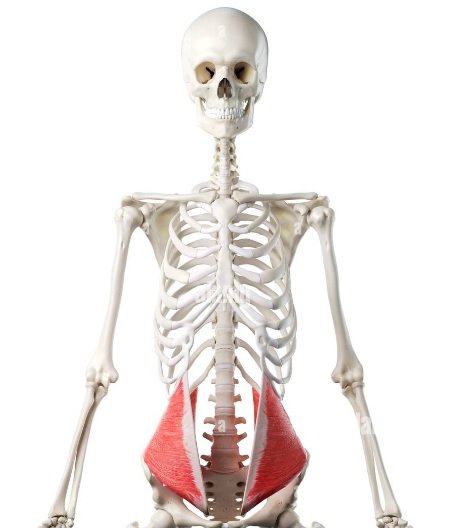
Quadratus Lumborum
These fibres originate on the iliac crest and insert on the transverse processes of first to fifth lumbar spine and the lower portion of the twelfth rib.
It acts to laterally flex the vertebral column, extension of the lumbar region of the vertebral column, elevates the ilium with ipsilateral contraction, and fixes the twelfth rib during forced expiration.
Psoas
These fibres originate on the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs of the 12th thoracic vertebra to the 4th lumbar vertebra, and the transverse processes of the 1st to 5th lumbar vertebrae and insert into the lesser trochanter of the femur as the iliopsoas tendon.
It acts to flex the thigh and trunk as well as lateral rotation of the thigh, and lateral flexion of the trunk.
Iliacus
These fibres originate on the iliac fossa and insert on the lesser trochanter of the femur.
It acts to flex and externally rotate the femur. It also helps to maintain body posture, and is a strong hip flexor when used with the psoas muscles.